What is Traceroute?
Overview
Traceroute is the most preferred tool that network engineers make use of to troubleshoot networks. It was innovated in 1987 and remains extremely relevant these days.
Traceroute may be a widely handed-down command-line benefit accessible in nearly all operating systems. It manifests you the entire route to a goal address. It also manifests the time is grasped or holdups in the middle of halfway routers. Isn’t it significant?
Scope
- This article discusses What is Traceroute, its use, and how to read a traceroute report.
- This article also discusses How Traceroute works and what they do?
- This article briefly focuses on the What is Traceroute Command in Linux and Other Operating Systems.
- This article also covers various Advantages of Traceroute and Challenges of Traceroute.
Introduction
Traceroute could be a command that runs tools utilized for network problem-solving. These tools trace down the pathways of data packets taken from their origin to their goals, permitting directors to resolve correspondence problems. On a Windows device, this instruction is termed as tracert; on Linux and Mac, it’s known as traceroute.
Traceroute and tracert mostly operate in the same manner—they depict the route information takes from one particular point in a connection to a determined IP server. Once information is communicated among two points, it should “hop” between many systems, such as switches and routers. Traceroute depicts every hop, supplies the main features and round-trip time (RTT), and offers the system name and IP address wherever practicable.
During ping will tell you if there is a fault, and traceroute will assist you to pinpoint wherever the matter obtains. For an associate example of how you may use traceroute, visualize you’re overtaking a website and its pages are taking an extended time to load. During this sample, you can use a traceroute to work out wherever the largest hinders are happening to get to the route of the difficulty.

What Does Traceroute Do?
A traceroute works by dispatching ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol messages, and each router is concerned with conveying the information obtained from these messages. The ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) messages give data regarding whether or not the routers utilized in the communication are able to productively transfer the information.
How Does Traceroute Work?
We can follow through the below diagram to get a better interpretation.

- First of all, the Source (Src) dispatches a message with .
- A Router lowers the TTL by one, which swaps the worth to 0. The message is released and the router dispatches ICMP TTL surpassed messages. The target IP address for the ICMP packet is identical to the origin IP address of the rejected packet. The origin IP address of the rejected message is the IP address of the intersection at which the message was accepted.
- The origin obtains the ICMP TTL Surpassed packet and attaches the router IP address to the Traceroute hops board.
- Then the method begins one more time with .
- The message is routed along with the primary Router R1, which conjointly declines the message price.
- The secondary Router R2 obtains the packet, decrements the TTL, discards the packet, and delivers the ICMP TTL Surpassed notification.
- And it pursues this by enhancing the TTL by one till it hits its goal destination.
What is Traceroute Used for?
An IP which stands for Internet Protocol tracer is used for determining the routing hops information must undergo, also as feedback hinders because it moves across nodes, which are anything that transmits the information toward its goal. Traceroute conjointly permits you to find wherever the information was inadequate to be sent ahead, called the positions of collapse. You are able to conjointly execute a visual traceroute to urge a visible illustration of every hop.
How to Run a Traceroute?
Prior to executing a traceroute command, you ought to perceive a network system referred to as Time To Live (TTL). Time To Live restricts regardless of how long information will live in the association of the Internet Protocol network. Each message of information is appointed a Time To Live price. Each time an information packet outreaches a hop, the Time To Live price is reduced by one.
One other key factor to grasp is Round-trip time (RTT). Traceroute makes sure every hop on the pathway to a goal implement releases a message and reverts back to an ICMP mistake message. This implies the traceroute will calculate the period of your time between once the information is distributed and once the ICMP packet is collected back for every hop—offering you the Round Trip Time worth for each and every hop.
To preferably illustrate this, presuppose you bound a traceroute and identify an utmost of thirty hops. Traceroute can transfer messages with a Time To Live(TTL) of 1 to the target server. The primary network tool is that the information that travels along can decrease the TTL to the value of 0, and an acknowledgment notifying you the messages were released is dispatched. This provides us the RTT for hop preference.
Accordingly, the information packets are dispatched to the target server with a TTL of 2. Because the messages move along with the primary hop, the TTL reduces to at least one. After that, they traverse through the 2nd hop, which reduces to zero. The message is distributed once more. This provides us the RTT for hop variety 2.
This method can be repeated till the information packets either get to the goal device or get to the most variety of hops.
- What if the router doesn't respond?
The inactivity diagnosed for every router in the trace is the time distinction between once the message is distributed and once the TTL surpassed message is obtained. It's mandatory to notice that there is no such obstacle for the router to dispatch that ICMP TTL surpasses the packet. Therefore if a router never discards the message, it is not invented in the traceroute, however since it is since reducing the TTL worth, it will be numbered as an unknowingly hop in the trace. Here is an illustration with hop #3 not transmitting ICMP TTL surpassed messages.
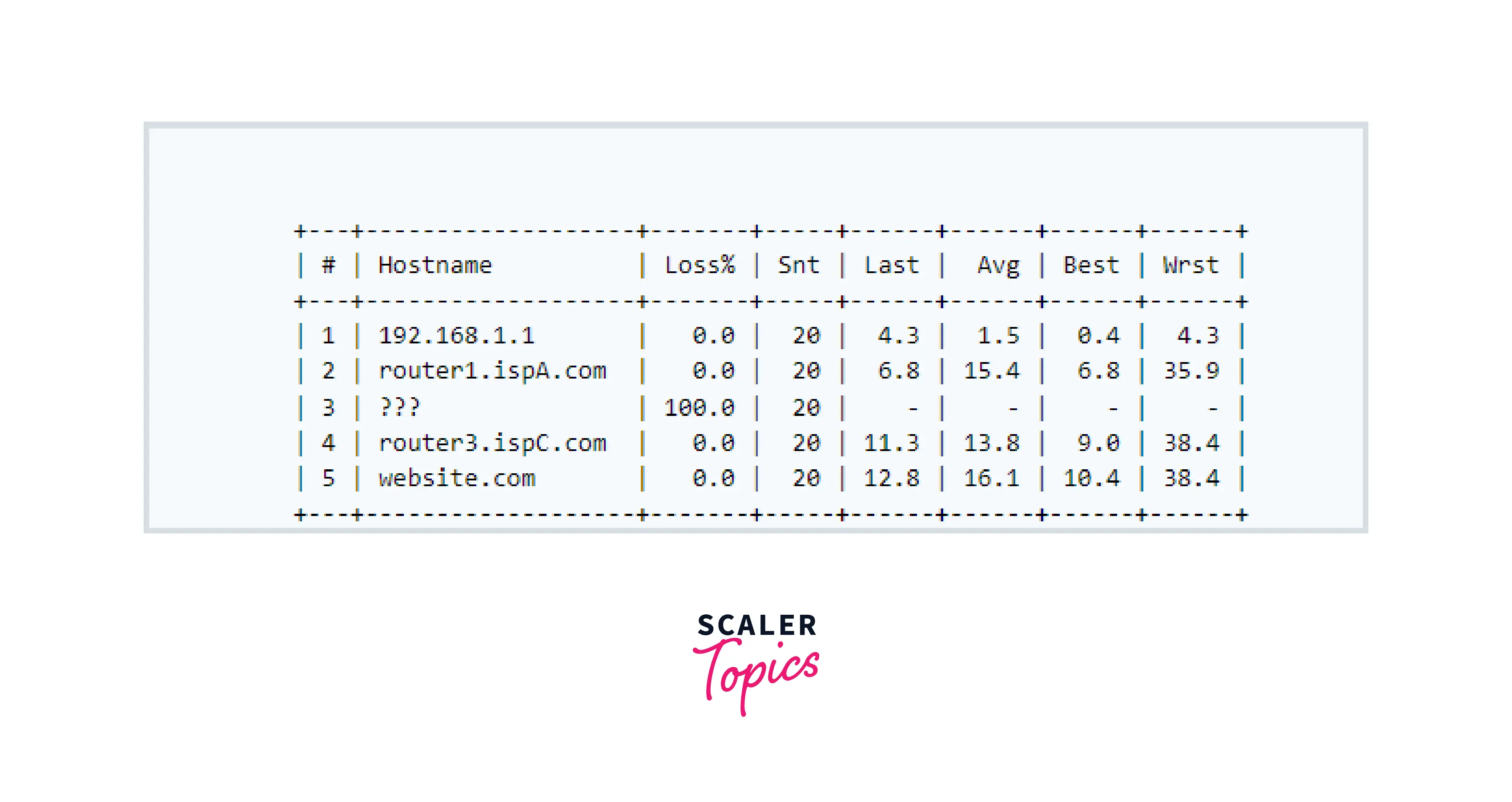
How to Read a Traceroute Report?
Traceroute outcomes can look marginally or completely different depending on the particular tool you utilize. If you select to utilize NetPat along with SolarWinds N-central, then scanning these outcomes is extremely easy. Intuitive visualization offers deep clarity—permitting us to troubleshoot hotspots over the delivery cycle.
If you utilize tracert, the Windows traceroute command, you will see the numerous quantity of hops from the origin device to the goal device within the far-left column. For every hop, we are able to see 3 RTT worth supplied by the TRACERT tool which was set to dispatch 3 data messages to check every hop, as per the default features. On the right, you ought to see extra system information.
Hops and Round Trip Times (RTT)
The traceroute reports items and information referring to each router the messages undergo as they move to their target location. The hops get counted on the left alignment of the report view window. Every line in the report holds the particular domain name—if that was involved—so is the IP location connecting to the router.
Tackling Traceroute Shortcomings
While a traceroute may be a great tool for characteristic issues, it will have some vital shortcomings. For example, it doesn’t show historical information, which might make building characteristic patterns troublesome. It conjointly doesn’t represent multiple methods easily—and as a result of several firewalls blocking ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) requests, traceroute typically displays incomplete information.
To overcome these shortcomings, it’s vital to seek powerful solutions which will supply deep visibility on the far side of what traceroute offers. NetPath may be a feature of the SolarWinds N-central suite, associate all-in-one remote observance and management answer designed with MSPs( Managed Services Providers) in mind. NetPath displays the flow of information in a very dynamic and visually compelling manner and may facilitate MSPs tackle the challenges historically related to traceroute. It conjointly options a professionally designed program as hostile to the tougher-to-know instruction show related to traceroute.
NetPath may perform as a far-off traceroute tool. To use the NetPath feature to perform a traceroute check, follow the below instructions:
- Navigate to the NetPath services page and click on “create new service”
- Fill in a very hostname or informatics address
- Fill in any transmission control protocol port
- Enter a nickname
- Enter an inquiring interval
- Click “next”
- Choose to either use the probe on your main polling engine or deploy a quest to a far-off location—this means that NetPath will perform as a far-off traceroute tool
- Click “create” to get your path
Choosing the Right Network Monitoring Tool
SolarWinds N-central is intended to relinquish MSPs access to increased capabilities, permitting them to achieve careful insight into client networks. This deep visibility helps improve their understanding of client terminus security and will increase technician potency therefore MSPs will expand their business.
As additional SMBs raise their MSPs to manage a patchwork of hosted, on-premises, and cloud services, the flexibility to spot the supply of IT problems becomes progressively tough. Mix this problem with the restricted management MSPs have over public cloud services, and this array of risks may result in client discontentedness.
NetPath was created to assist MSPs address these problems. It’s a visible and intuitive feature that offers you insight into your customers’ expertise of slowdowns once making an attempt to access a network service or website. To find out additional, get N-central free for thirty days to start exploring.
What is Traceroute Command in Linux and Other Operating Systems?
Meaning of the tracert command result.
Let’s explore what the came back results of a tracert command suggests. To do this, we tend to head straight to our prompt or terminal.
Let’s produce a traceroute to scaler.io. we tend to do that by getting into the subsequent command in our terminal or command prompt:
For Windows:
tracert www.scaler.io
For Linux/Mac:
traceroute www.scaler.io
Output:
The output may seem like the diagram below:
 )
)
Are Traceroute and Tracert the Same?
Traceroute and tracert accomplish a similar general operation. The sole important distinction is that the command is traceroute on Mac and UNIX/LINUX operating system systems and tracert on a Windows system.
Advantages of Traceroute
- It will verify the reason for a response delay in a very network.
- It determines the routing loops gift in a very network pathway across nodes that send and receive packets.
- It finds the situation of failure points within the network whereas packets move from supply to destination.
Challenges with Traceroute commands for today’s networks
1. Asymmetric ways can not be seen simply. Solely A-to-B is rumored by default. B-to-A needs another traceroute from the opposite end to complete the trail.
Asymmetric routing may be commonplace in networks nowadays. There area unit several equal-cost multi-path (ECMP), and even unequal value multi-path routing protocols live, and betting on the hashing rule, traffic can seemingly take a special path in every direction. These totally different ways are terribly tough to sight with one traceroute command execution, and so terribly tough to sight specifically wherever the delay result's coming back from being wedged.
As you'll be able to see on top of this, the delayed price jumps up at this specific hop, however, the question is “where is that delay?” Is it on the forward path, or on the come path?
2. : Interfaces don't seem to be acknowledged, solely the device information processing node. There's no further detail.
If we glance at the traceroute on top once more, the sole info provided may be a hostname/IP and a delayed result. If a user were to analyze hop half dozen, they'd got to telnet/ssh to the router, and verify that interface this IP address was hooked up to. Secondly, to work out the egress (outgoing) interface, a second look-up would wish to be completed to work out this info.
3. : Traceroute depends on ICMP electronic communication which can report an extended delay than is truly perceived by traffic since they're processed on the “slow path” of a tool vs. the “fast path” that's accustomed to forward knowledge passing through the router.
Slow-path is most simply summarized as once the router has to method the contents of the packet. Just about any packet that's destined for a tool is handled in this manner. Newer routers have internal mechanisms to order the packets they method (routing protocol updates before ICMP messages), however, this solely will increase the difficulty here. As we’ve mentioned earlier, most systems can use a UDP message, but the act of generating the ICMP TTL expired message may be a lower priority than the come path going to be Associate in Nursing ICMP message, therefore the delay metrics provided within the results area unit tough to simply accept as real issues.
TIP: once you see a traceroute that jumps at a selected step within the result and everyone following results are unit low, this can be a sign that the slow router is delayed in the process. If the trail jumps then every following step on the trail is incremented, this usually means some variety of queuing because of congestion.
4. : Traceroute output is the static text that can't be acted upon simply.
Alright, therefore currently we all know the trail toward a particular destination, however, what if I need to dive deeper into one or a lot of hops on that path? Telnet/SSH console sessions would require the user to log into these devices. The interface information processing address is provided within the traceroute response. This could create a challenge in several networks, since, from a security policy perspective, users should telnet/ssh to the management information processing address. Telnet may well be blocked on the precise interfaces being rumored within the traceroute, which needs some variety of manual search to work out the management interface of a tool therewith interface address, but without DNS resolution, this could be nearly impossible. Once there's an example outage, each second may be counted against you.
Conclusion
- NetBrain’s PDA System includes a wealth of automation and mental image options needed to keep up with fashionable networks.
- It acknowledges software-explained, virtualized, and also the cloud. It unceasingly communicates with each device on the end-to-end network and builds a period of time digital twin of the network.
- This digital twin is an explicit duplicate of the main points of each device. It includes the flexibility to see the period of time networks and includes a contemporary replacement for traceroute, remarked because of the A/B Path Calculator.
- This addresses these challenges by serving to engineers dynamically map a network path between any 2 points within the network and supply extreme detail of that path.
- This PDAS operation supports mapping through fashionable technologies (e.g. SDN, SD-WAN, firewalls, load balancing), underlays, and overlays, all whereas considering advanced protocols (routing, access lists, PBR, VRF, NAT, etc.).
- And once PDAS is deployed, a constant structure that may be visualized in the period of time currently creates the proper platform for no-code automation of each task, massive and small!
